BlueZone partners with over 50
world-leading original equipment
manufacturers and systems providers
C-Dye 370
Ultraviolet leak tracing dye
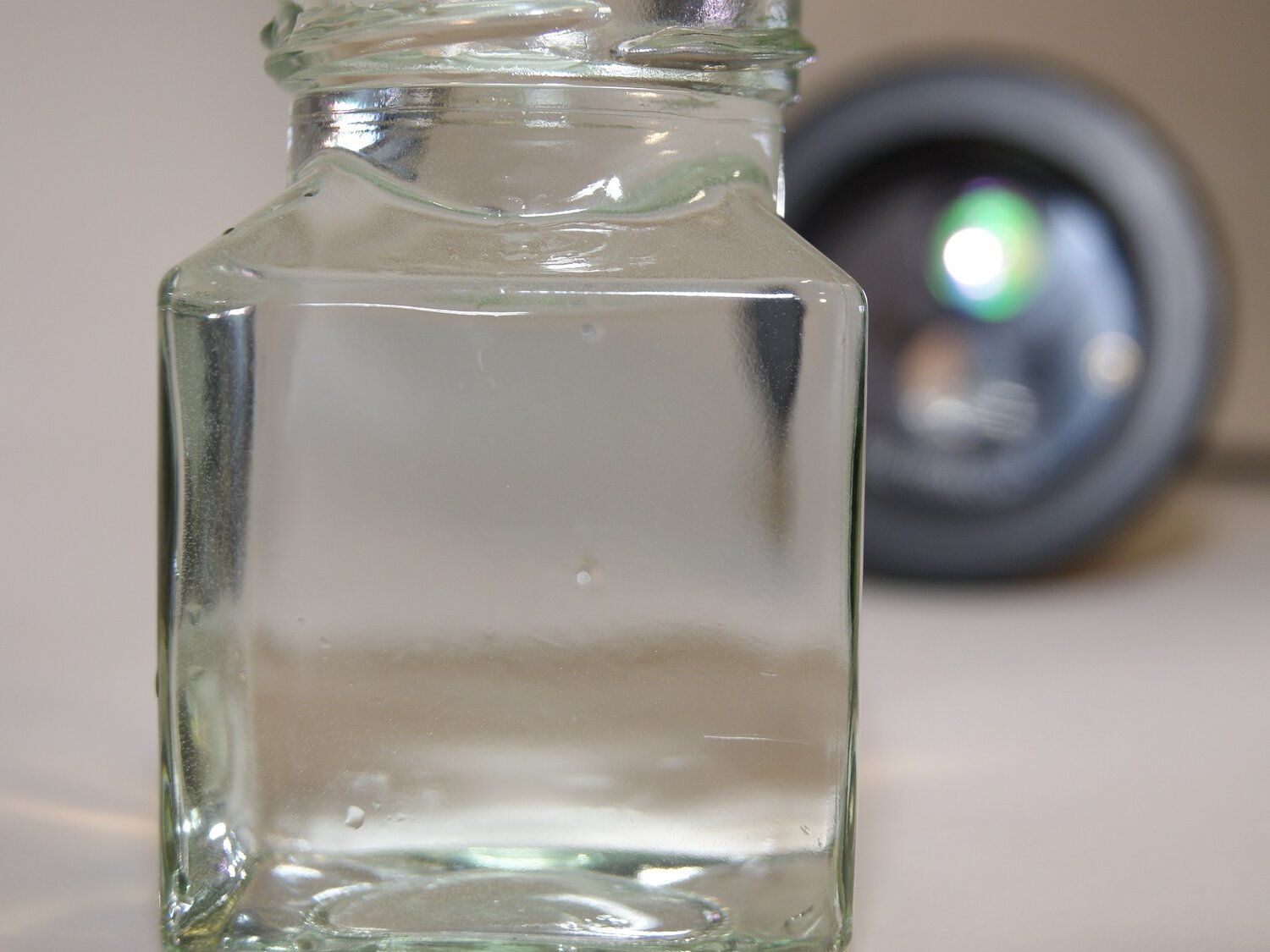
OceanTools C-Dye 370 is a colourless UV dye concentrate, designed for tracing leaks in a variety of subsea environments. With maximum absorption in the near UV range and emission in the visible range, it can help identify leaks around subsea control systems, risers and pipelines.
The dye is typically dosed at a ratio between 100ppm and 200ppm depending on the application. Compatibility with the dosage medium and the appropriate concentration should be confirmed prior to use, and the dye should be thoroughly dispersed within the chosen medium. C-Dye 370 is registered with CEFAS in the UK (OCNS Gold / OCNS Class D) and the Netherlands (HMCS Pre-screening Category C) and has a substitution warning. It is also registered for use in Denmark and Norway.
OceanTools C-Dye 370 Safety Data Sheet
For more information about OceanTools C-Dye 370, Contact the team at BlueZone.
Key Features
Up to 25-hour mission duration
Speeds up to 4.2 knots
Increased module payload capacity
Search and recovery
Hydrography
Deep sea mineral exploration
Marine & Fisheries research
Product Enquiry
Related products
DeepSea Power & Light's Multi SeaLite is their most popular halogen light and has been in production for over 20 years.
Read moreSS455 Hyperbaric IR HD Video Camera
The SS455 Hyperbaric Video Camera provides a 12MP 187° field of view (FOV) with digital zoom, double, and single panorama, or quad view for superior situational video surveillance. Motion detection,...
Read moreBowtech has designing, manufacturing and supplying products to the subsea ROV, AUV, Defence, Nuclear and Leisure markets for over 20 years. From patented designs through to unique manufacturing techniques, Bowtech...
Read moreRelated Articles
Precision Under Pressure: BlueZone’s Eight‑Day Subsea Success
Eight Days, Ten Cables, One Epic Holiday Turnaround While most businesses were winding down for the holidays, BlueZone was powering up. As December 2025 raced toward Christmas, our workshop...
Read MoreRapid, Reliable, Ready: The Littoral Riverine Survey System in Defence Hydrography
When military operations hinge on understanding what lies beneath the waves, deployable hydrographic survey systems like the LRS become essential tools for safe, informed decision‑making. Military hydrographic...
Read MoreKraken MP‑SAS: Portable Synthetic Aperture Sonar for Modern Maritime Missions
With Kraken’s MP‑SAS and BlueZone Group’s trusted in‑country support, Australian operators can now access a proven, portable SAS solution built for modern maritime missions. As the demand...
Read More